Project 9 (2025-2028)
Microglial diversity in the remodeling of GABAergic synapses in corticolimbic circuits and anxiety-related behaviors
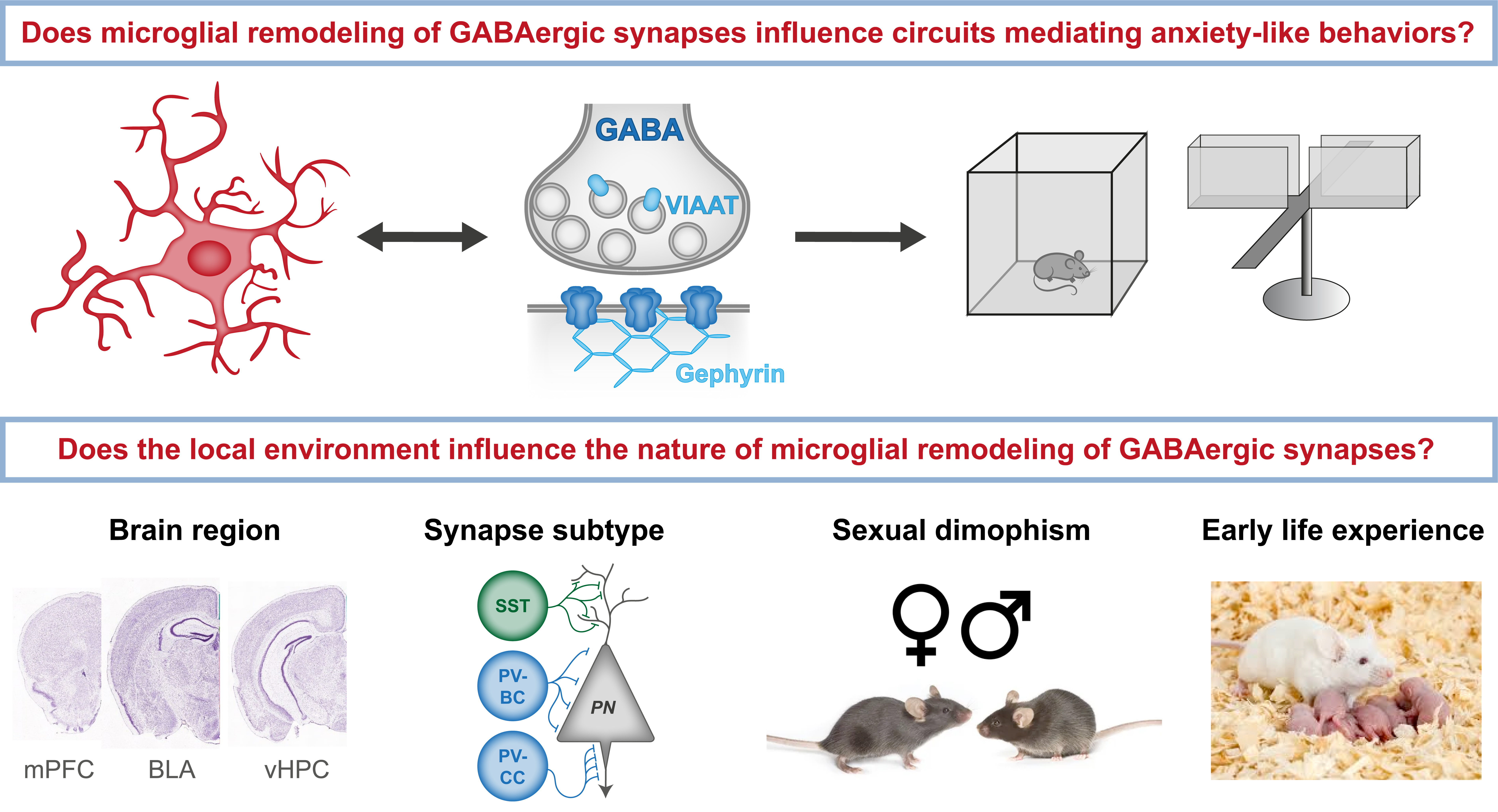
Microglia play an extraordinarily wide range of roles in shaping brain function both under physiological and pathological conditions. Unsurprisingly, therefore, altered microglial activity has been increasingly linked to the etiology of psychiatric disorders in recent years. It has been postulated that microglia may contribute to these disorders either through aberrant activation and inflammatory responses, potentially induced by stress, or due to loss of normal physiological processes that shape and maintain healthy brain circuits.
One key process mediated by microglia under both physiological and pathological conditions is synapse remodeling. While most studies have focused on microglial remodeling of glutamatergic excitatory synapses, recent evidence indicates that that they contribute equally to the remodeling of GABAergic inhibitory synapses. Given the link between GABAergic synapse dysfunction and psychiatric disorders, including anxiety disorders, uncovering the precise mechanisms by which microglia shape GABAergic synapses is essential for understanding their role in psychiatric disorders.
Based on this notion, the central objectives of the current proposal are to determine whether microglia may contribute to the etiology of anxiety-related disorders through their role in remodeling of GABAergic synapses in the developing corticolimbic system, and to investigate whether the local environment influences microglial remodeling of GABAergic synapses under physiological and stress-induced pathological conditions. To this end, we will combine a wide range of approaches in mouse models, including immunohistochemistry, electrophysiology, optogenetics, chemogenetics, RNA sequencing and in vivo imaging. The ultimate aim of this research is to identify potential therapeutic strategies to target aberrant microglial remodeling of GABAergic synapses in psychiatric disorders.
 SPP2395 PREMIER Wiki
SPP2395 PREMIER Wiki